Network Automation
14 Dec 2020
Automation Overview
Automation is any process that is self-driven, that reduces and potentially eliminates, the need for human intervention.
- work 24 hours a day, which results in greater output.
- produce a uniform product.
- collection of data that can help guide an event or process.
- used in dangerous conditions reducing the risk to humans.
- alter their behaviour to reduce energy usage, make a medical diagnosis, and improve automobile driving safety as examples
Data Formats
JSON - JavaScript Object Notation
- Simpler and more readable than XML
- Hierarchical structure and contains nested values
- Uses colon separated key value pairs
- Keys must be strings within double quotation marks “ “
- Supports strings, number, Boolean, arrays and objects
- {} defines an object and [] defines an array
- Whitespace is ignored
Example
{
"ietf-interfaces:interface": {
"name": "GigabitEthernet2",
"description": "Wide Area Network",
"enabled": true,
"ietf-ip:ipv4": {
"address": [
{
"ip": "172.16.0.2",
"netmask": "255.255.255.0"
},
{
"ip": "172.16.0.3",
"netmask": "255.255.255.0"
},
{
"ip": "172.16.0.4",
"netmask": "255.255.255.0"
}
]
}
}
}
YAML - YAML Ain’t Markup Language
- Simpler and more readable than XML and JSON
- Uses colon separated key value pairs, no commas and no quotes
- Hyphen is used to separate each element in a list
- White defines the structure
- Indentation is important for defining objects
- Assumes the data type
- Considered a superset of JSON.
Example
ietf-interfaces:interface:
name: GigabitEthernet2
description: Wide Area Network
enabled: true
ietf-ip:ipv4:
address:
- ip: 172.16.0.2
netmask: 255.255.255.0
- ip: 172.16.0.3
netmask: 255.255.255.0
- ip: 172.16.0.4
netmask: 255.255.255.0
XML - eXtensible Markup Language
- Designed for internet and looks like HTML
- Hard to read - designed to carry data not read it
- Uses tags to structure
- Tags can have attributes
- Whitespace is ignored
- Self-descriptive, encloses data within tags
Example
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<ietf-interfaces:interface>
<name>GigabitEthernet2</name>
<description>Wide Area Network</description>
<enabled>true</enabled>
<ietf-ip:ipv4>
<address>
<ip>172.16.0.2</ip>
<netmask>255.255.255.0</netmask>
</address>
<address>
<ip>172.16.0.3</ip>
<netmask>255.255.255.0</netmask>
</address>
<address>
<ip>172.16.0.4</ip>
<netmask>255.255.255.0</netmask>
</address>
</ietf-ip:ipv4>
</ietf-interfaces:interface>
Application Programming Interface (API)
https://developer.cisco.com/video/net-prog-basics
An API is software that allows other applications to access its data or services. It is a set of rules describing how one application can interact with another, and the instructions to allow the interaction to occur.
Popular APIs
- SOAP
- Mature API
- Used to build internet web services
- Uses HTTP and XML
- REST
- API framework
- Simpler and more flexible than SOAP
- Uses HTTP with JSON and XML support
- NETCONF
- Designed to replace SNMP between management programs and network devices
- Uses SSH and XML
- RESTCONF
- REST like API to the network
- Supports XML and JSON
- Defines transport and communication and is coupled to YANG for data stores
A web service is available over the internet. There are four types of web service APIs:
- Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) - older
- Representational State Transfer (REST) - newer
- eXtensible Markup Language-Remote Procedure Call (XML-RPC) - developed before SOAP
- JavaScript Object Notation-Remote Procedure Call (JSON-RPC) - similar to XML-RPC
RPC is when one system requests that another system executes some code and returns the information.
REST
A framework for creating web APIs built on HTTP/HTTPS
RESTCONF is a REST-like API for managing and configurating network devices using HTTP
How to execute a REST API request?
- Web Browser - HTTP
- Command Line - CURL
- Application - POSTMAN
- Programming Language - Python, JavaScript, Ruby, and more…
HTTP client/server request and response methods
- POST - Create
- GET - Read - request
- PUT/PATCH - Update
- DELETE - Delete
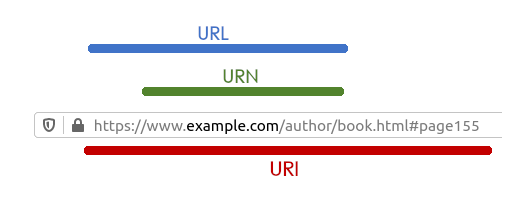
REST APIs use Universal Resource Identifier (URI) to identify a server resource.
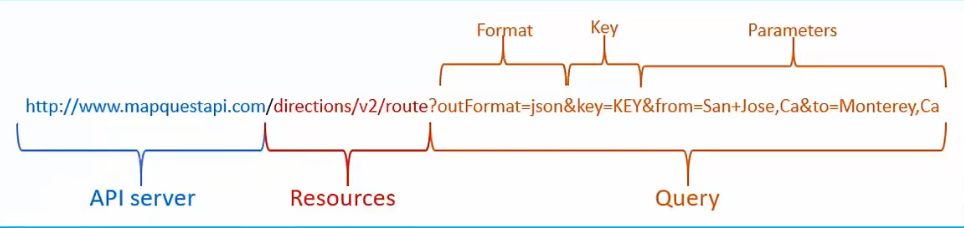
An API can be considered “RESTful” if it has the following features:
- Client-Server - The client handles the front end and the server handles the back end.
- Stateless - No client data is stored on the server between requests. The session state is stored on the client.
- Cacheable - Clients can cache responses to improve performance.
Parts of a URI
Configuration Management Tools
Configuring a device using CLI is manual, time consuming and prone to errors
SNMP is excellent for monitoring devices but typically not used for configuration due to security and difficulty of implementation.
Configuration management tools make use of RESTful API requests to automate tasks and can scale across thousands of devices.
Ansible
- Python and YAML
- Agentless
- Any Device Controller
- Uses a Playbook
SaltStack
- Python
- Agent-based and Agentless
- Salt Master Controller
- Uses a Pillar
Puppet
- Ruby
- Agent-based and Agentless
- Puppet Master Controller
- Uses a Manifest
Chef
- Ruby
- Agent-based
- Chef Master Controller
- Uses a Cookbook
Automation is typically associated with a tool automatically performing a specific task.
Orchestration is arranging a set of automated tasks that results in a coordinate process or workflow.
Intent-Based Networking (IBN) and Cisco DNA Center
IBN builds on Software-Defined Networking (SDN)
Business objectives for the network are expressed as intent. IBN captures business intent and uses analytics, machine learning, and automation to align the network continuously and dynamically as business needs change.
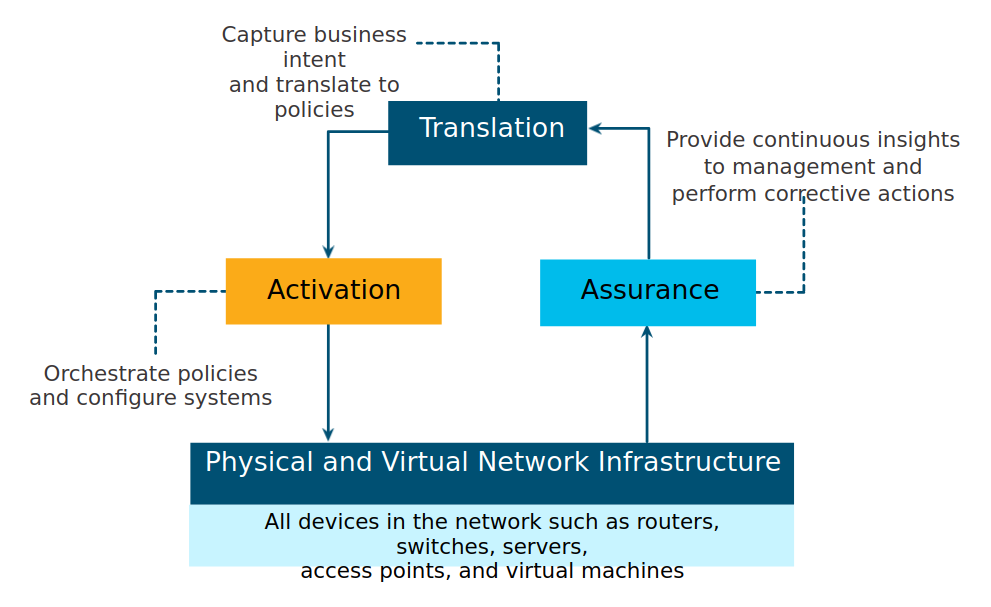
From the perspective of IBN, the physical and virtual network infrastructure is a fabric.
the overlay is where encapsulation protocols like IP security (IPsec) and Control and Provisioning of Wireless Access Points (CAPWAP) occur.
The underlay network is the physical topology that includes all hardware required.
Cisco’s IBN is implemented using Cisco’s DNA
Cisco DNA is a system that is constantly learning, adapting to support the business needs.
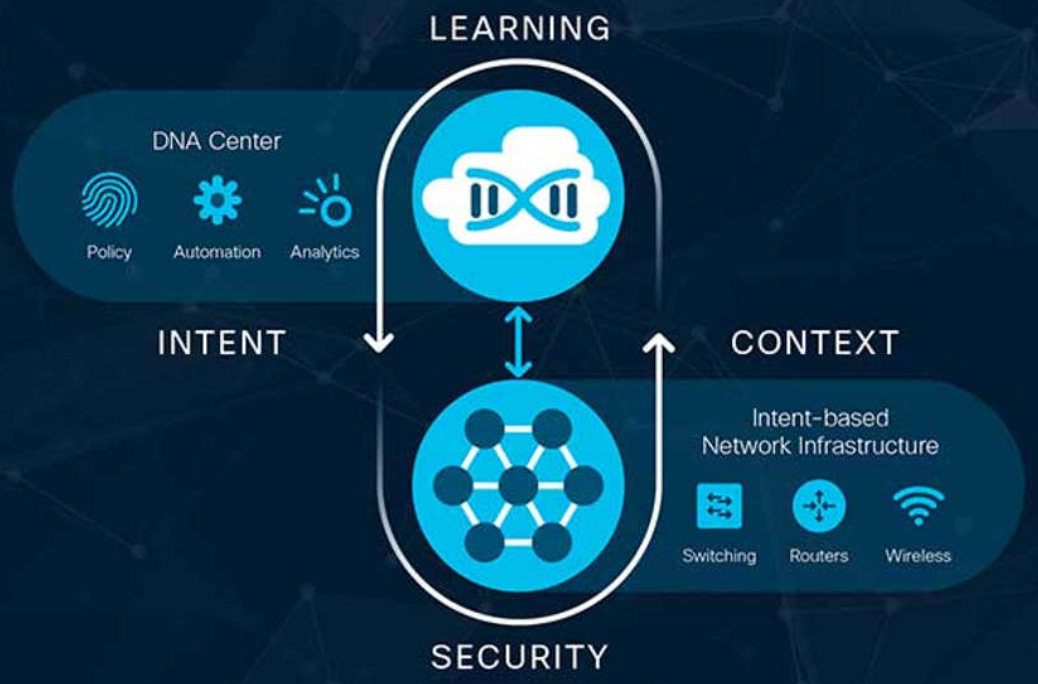
The business intent is securely deployed into the network infrastructure (the fabric). Cisco DNA then continuously gathers data from a multitude of sources (devices and applications) to provide a rich context of information. This information can then be analyzed to make sure the network is performing securely at its optimal level and in accordance with business intent and network policies.